Mastering SEO Content + Downloadable SEO Copywriting Cheat Sheet
For the purposes of this article we will mainly focus on Google as they are still dominating the search space, however many of these areas will be helpful to keep in mind regardless of the search engine or platform.
This guide is here to equip you with the strategies and steps needed to create SEO content that ranks well on Google and other search engines while keeping your audience engaged. We’ll cover everything from the basics of keyword research to advanced on-page optimisation techniques, ensuring that you have a complete toolkit to improve your content’s search performance.
Many guides cover SEO, but this one is designed to bridge the gap between beginner concepts and advanced techniques that are often overlooked. We’ll break down complex topics into actionable steps and introduce some innovative tips that aren’t always included in the standard SEO playbook.
Plus, to make the process easier, we’re offering a downloadable SEO Copywriting Cheat Sheet, so you can apply what you learn here directly to your content.
Download your SEO Copywriting Cheatsheet
Let’s jump into creating SEO content that makes an impact!
Part 1: Understanding SEO Content
What is SEO Content?
SEO content is any type of online material created with the goal of ranking in search engine results. Whether it's blog posts, product pages, videos, or infographics, SEO content is crafted to attract organic traffic through search engine visibility. It’s not just about using keywords but about making content that genuinely helps and engages readers.
Types of SEO Content
Blog Posts: Foundational pieces that can cover trending topics, tutorials, or in-depth guides, perfect for driving consistent traffic.
Product Pages: Important for eCommerce sites, optimised product pages help potential customers find what they need.
Landing Pages: These pages are focused on conversion, so SEO here involves both visibility and clear calls to action.
Infographics and Visual Content: Great for capturing attention quickly and increasing shareability.
Videos: Video content is on the rise, with platforms like YouTube also serving as search engines.
Add Value: Include formats often overlooked, such as interactive content (quizzes, polls) and user-generated content (reviews, comments) that engage visitors while still enhancing SEO.
Key Elements of SEO Content
Relevance: Every piece of content should address a need or question from your target audience.
Keyword Strategy: Knowing and using keywords that match your audience’s intent.
User Experience (UX): Search engines consider how users interact with content, so design for easy readability and navigation.
Part 2: Researching and Selecting Keywords
To create content that truly resonates with readers and ranks well in search engines, it all starts with understanding and selecting the right keywords. Keyword research isn’t just about picking popular words or phrases; it’s about understanding what your audience needs and aligning with their search intent.
Let’s look at how to do keyword research effectively, making sure you’re targeting terms that can help you rank, attract the right audience, and ultimately, achieve your content goals.
User Intent and Keyword Research
Understanding user intent is the foundation of effective keyword research. When users type a query into Google, they have a specific intention behind it. In SEO, user intent is looking for what the searcher is trying to accomplish with their search. Understanding this intent helps make sure your content is going to satisfy their needs, this could be anything from learning more about a topic, finding a specific brand, to making a purchase and comparing alternatives.
There are three main types of user intent you’ll want to keep in mind:
Informational Intent: These users are seeking knowledge. They may want answers to questions, detailed explanations, or how-to guides. A keyword like “how to improve website SEO” shows informational intent because the user is likely looking for helpful content on that topic.
Navigational Intent: Users with navigational intent want to go to a specific website or page. For example, a search for “Bunnings blog” or “Facebook login” is clearly intended to take the user to that destination.
Transactional Intent: These users are ready to make a purchase or take an action, often including keywords like “buy,” “discount,” or “free trial.” A search for “buy SEO tools online” or “best SEO tools 2024” indicates transactional intent.
To align your content with user intent:
Identify the intent behind your primary keywords and tailor your content to answer the specific needs of that intent.
Choose keywords that match the purpose of your content (e.g., use informational keywords for blog posts and transactional ones for product pages).
Use intent modifiers in your keyword selection to refine intent (e.g., “best,” “top,” “how to,” “buy,” “near me”).
Aligning keywords with user intent, means that your content will be more likely to satisfy searchers’ needs and rank higher in relevant search results.
Pro Tip: When conducting keyword research, note that keywords with informational intent tend to be broader and generate more traffic, while transactional keywords are usually more specific and lead to higher conversions.
How to Do Keyword Research & Helpful Tools
Keyword research can be broken down into a few key steps, each designed to uncover valuable search terms that resonate with your audience and support your SEO strategy.
1. Start with a Seed Keyword List
Begin with basic terms related to your industry or topic. For example, if you’re writing about SEO, your initial list might include “SEO tips,” “keyword research,” and “content optimisation.”
Think about the problems, questions, and interests of your target audience. These ideas will form the foundation of your keyword research.
2. Use Keyword Research Tools to Expand Your List
Ahrefs: Enter your seed keywords to find related terms, their search volumes, and keyword difficulty. Ahrefs’ “Keyword Explorer” and “Content Gap” tool can help identify opportunities by comparing keywords you aren’t ranking for but your competitors are.
SEMrush: This tool provides search volume, trends, and difficulty for each keyword, plus insights on competitors’ keywords. Use the “Keyword Magic Tool” to discover groups of related keywords based on your seed list.
Google Keyword Planner: Although it’s primarily used for PPC campaigns, Google Keyword Planner is a free tool that gives valuable information on search volumes and keyword trends. Use it to get a baseline of keyword popularity and refine from there.
3. Analyse Keyword Metrics to Select the Best Terms
Search Volume: Higher search volumes mean more people are searching for that keyword, but don’t focus only on volume; consider relevance.
Pro-Tip: Look for keywords with high search volume but moderate competition so that you are more likely to rank and rank faster.
Keyword Difficulty (KD): This score indicates how hard it is to rank for a keyword based on the competition. Start with lower-difficulty keywords if your site is new or still growing.
Click-Through Potential: Not all keywords with high search volume drive clicks. Consider how likely a searcher is to click on a result, especially if the SERP has many ads or featured snippets that answer the query directly.
Selecting Your Target Keywords:
Focus on Relevance: Ensure that your keyword aligns with the topic and intent of your content.
Evaluate Keyword Difficulty: Choose keywords within reach by balancing search volume and competition. Tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush can help.
Use Related Keywords: Diversify with synonyms and related phrases to capture a wider audience without relying on one keyword.
4. Refine Your Keywords with Long-Tail Phrases
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases (3+ words) that are often less competitive and reflect clear user intent. While “SEO” might be a tough keyword to rank for, “SEO tips for small business owners” or “beginner SEO checklist” is more targeted and often easier to rank.
How to Find Long-Tail Keywords:
Google’s Autocomplete: Start typing your seed keyword in Google, and note the longer, more specific phrases Google suggests.
People Also Ask and Related Searches: Google’s “People Also Ask” section and “Related Searches” at the bottom of the page are great sources for long-tail variations.
Use Tool Filters: Many tools, like Ahrefs and SEMrush, allow you to filter keywords by length or difficulty to focus on long-tail opportunities.
Using Long-Tail Keywords: These keywords often work well in blog post titles, subheadings, and within the body text. They help with targeting readers who have specific needs or questions, and they can help boost rankings for niche queries.
Content Gap Analysis
Once you have a solid list of keywords, it’s time to level up your strategy by performing a content gap analysis. Content gap analysis is a way of identifying keyword and topic opportunities that your competitors are targeting, but you haven’t covered yet.
Here’s how it works:
Find Your Main Competitors: Use SEO tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to enter your website and see which sites are ranking for similar topics.
Use the Content Gap Tool: Tools like Ahrefs’ “Content Gap” feature let you enter competitors’ URLs alongside your own to highlight keywords they’re ranking for that you aren’t.
Identify Missing Keywords: Look for keywords that have moderate to high search volume and relevance to your content goals.
Plan New Content or Update Existing Content: Once you have a list of gap keywords, use them to come up with new content ideas or add them to existing pieces. Closing these gaps can help improve your rankings by filling in valuable content areas your competitors are already covering and providing a more complete and valuable piece of content.
After identifying gaps, create content clusters around these keywords to establish and strengthen your topical authority and improve the likelihood that you will rank for related keywords (since Google is more likely to see you as a knowledgeable source).
For example, if you identify a gap in “local SEO,” create a series addressing “local SEO for small businesses,” “local SEO tips,” and “best local SEO tools” to cover the topic in more detail. This strategy helps you build a comprehensive content strategy around topics your competitors have already seen success with, filling gaps and increasing your reach.
Part 3: Content Quality: E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
Google’s algorithm is constantly changing, but one principle remains at its core: providing users with the best possible experience (or trying hard to…). That’s where the E-E-A-T guidelines come in.
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness, and it’s how Google assesses the overall quality of a website’s content. High E-E-A-T signals to Google that your content is credible and worth ranking higher in search results. While it is not a direct ranking factor it is an important element and a key component to creating content that is designed for people, rather than just search engines.
So, how do you create content that hits all the E-E-A-T marks? It honestly starts with having a deep understanding of your audience, their pain points, struggles, and their needs. Content that demonstrates your expertise in a particular field, backed by reliable sources and data, is far more likely to rank well. For example, long-form guides, how-to articles, and detailed case studies are usually good candidates for satisfying E-E-A-T criteria because they typically offer in-depth, useful information that answers user queries comprehensively.
But don’t fall into a trap of thinking that E-E-A-T is just about having the right keywords in your content. It’s important to create authentic, well-researched content that builds trust with your audience. When your content consistently delivers value, Google is more likely to recognise your site as an authority in your industry or niche.
Knowing how Google evaluates the relevance and usefulness of the content you’re putting out there is an important part in understanding how content supports SEO. Google uses what they call the "Needs Met" scale, which helps determine how well a page meets a user’s search intent.
At one end, you have the Fails to Meet rating – where the content completely misses the mark. This usually happens when the content is off-topic or doesn’t address the query at all. Think of it as the digital equivalent of asking for information on Batman (from the example above) and being shown results for a place called Batman – really missing the mark.
Then, you’ve got Slightly Meets, which is content that maybe touches on the query but doesn’t provide much value. It might work for a small, niche query but won’t fully satisfy a broader user base.
As you move up the scale, there’s Moderately Meets – this is where content does a decent job of answering the query but could do more. It’s helpful, but not comprehensive.
Highly Meets is where your content really starts to shine. It’s relevant, useful, and provides a lot of value to users. When your content falls into this category, you’re in a good position to rank well.
Finally, at the top of the scale is Fully Meets – this is the gold standard. Your content completely satisfies the user’s query and leaves little to no room for doubt. It’s the kind of content Google loves to put right at the top because it answers the question in the most complete and precise way.
Why does this matter? Because the more your content meets user intent, the better your chances are of ranking higher in search results. By aligning your content with the needs of your audience, you get a win-win for SEO and providing a better user experience – two birds, one stone (although we definitely do not condone throwing stones at birds, you get the point).
Part 4: Actionable Steps to Improve Your SEO-Content Strategy
Now that we’ve covered the fundamental principles and tactics, it’s time to focus on taking action.
Knowing what to do is one thing, but knowing how to do it can elevate your strategy from good to exceptional. This section is all about rolling up your sleeves and putting these insights into practice with a series of actionable steps that can turbocharge your SEO content strategy.
Let’s get into the nitty gritty parts of optimising, repurposing, and how you can leverage AI to lighten the load and support your growth.
📝 Creating Content with Optimisation in Mind
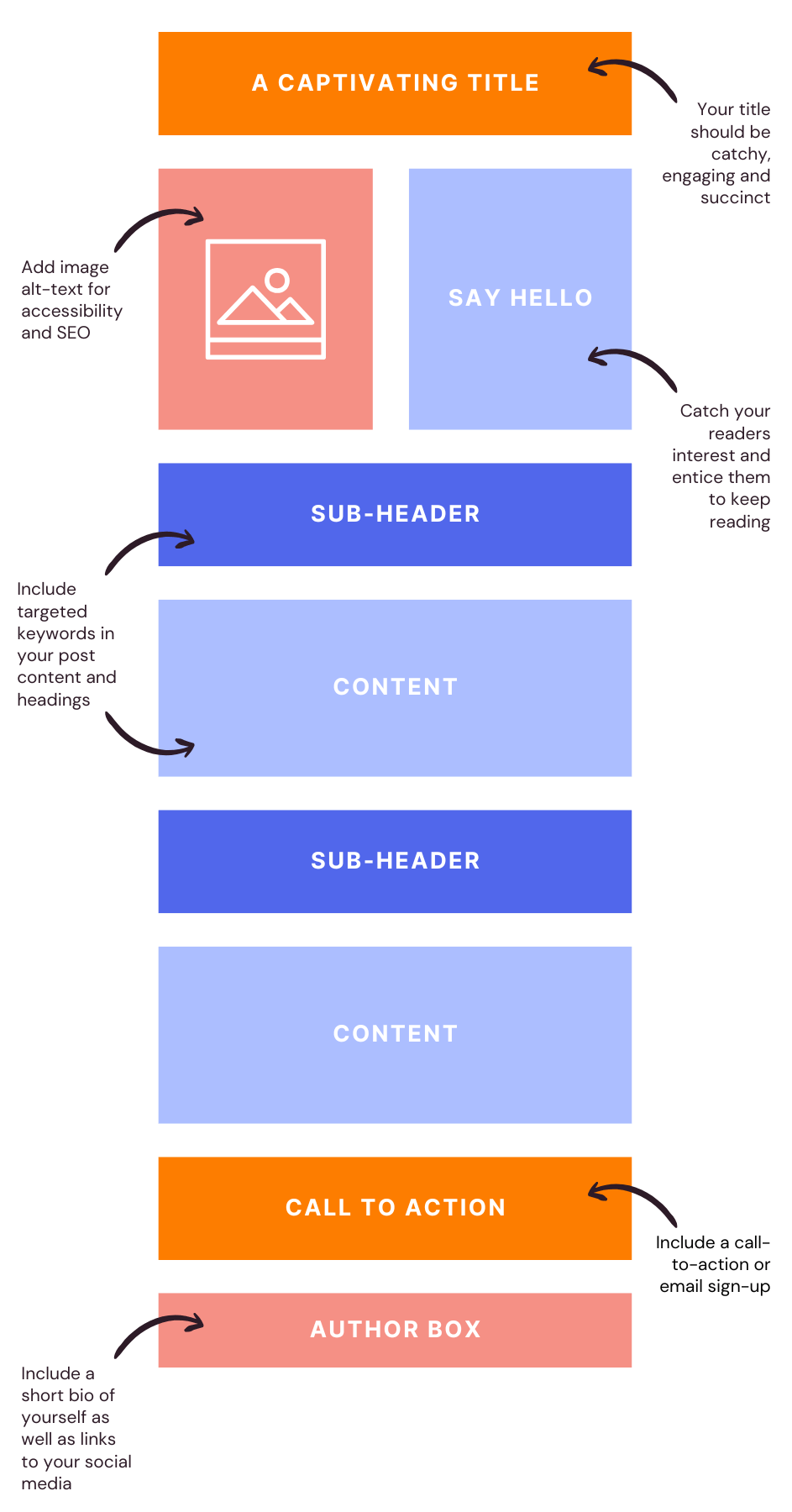
Creating content that ranks well isn’t just about keywords and backlinks; it’s about delivering a seamless, enjoyable experience for readers while keeping best practices in mind. Here, we’ll walk through the important parts of optimising your content so it’s as engaging and accessible as it is SEO-friendly. From writing better titles to optimising visuals, these strategies will help your content perform well in search and provide real value to your audience.
Engagement and Readability Tips
Great content doesn’t just inform; it also engages. To hold a reader’s attention, your content needs to be easy to read, well structured, and visually approachable and not overwhelming.
Here’s some tips on how to make sure your content that’s as engaging as it is informative:
Use Subheadings: Subheadings (like H2 and H3 tags) break up your content into digestible chunks, making it easier for readers to skim and find the information they need. Subheadings can also signal important keywords and topics to search engines, boosting SEO.
Keep Paragraphs Short: Large blocks of text can be overwhelming causing readers to click away. Aim to keep paragraphs to 3-4 sentences, making it easy for readers to move through your content.
Incorporate Bullet Points and Numbered Lists: When covering steps, key points, or comparisons, using bullet points or numbered lists can help communicate ideas quickly. They’re also visually appealing and make the content feel organised and easy to follow.
Choose Simple, Clear Language: Avoid jargon or overly complex language, especially if your audience is unfamiliar with the topic. The clearer your language, the more accessible your content will be.
Use Images and Visual Breaks: Adding relevant images, infographics, or videos enhances the reader’s experience and breaks up text-heavy sections. Visuals also improve time on page, a factor Google considers in ranking.
Writing Page Titles and Meta Descriptions
Your title and meta description are the first impressions your content makes in search results, and they play an important role in whether someone clicks on your link.
Here are some tips for writing titles and meta descriptions that are both SEO-friendly and enticing to readers:
Use Primary Keywords Naturally: Include your main keyword at the start of your title if possible. This helps both search engines and readers immediately understand the topic.
Make It Descriptive and Accurate: Your title should reflect what the reader will gain from clicking on your link. Avoid clickbait or misleading titles, as they can lead to high bounce rates (and frustrated readers).
Incorporate Power Words: Words like “Ultimate,” “Essential,” “Complete,” and “Guide” often catch attention. They give readers the impression that your content is thorough and authoritative. This obviously isn’t an exhaustive list but can give you a starting point, as with anything in SEO it is recommended to test and experiment with what works best for your audience and in your industry.
Optimise Meta Descriptions: Although meta descriptions aren’t a direct ranking factor, a good description can work wonders for improving click-through rates. Try to aim for around 155–160 characters, include your primary keyword (without forcing it, natural flow is more important), and summarise what the content covers.
Example: If your topic is “SEO Tips for Beginners,” a strong title and meta description could be:
Title: “SEO Tips for Beginners: A Complete Guide to Ranking Higher in 2024”
Meta Description: “Looking to boost your site’s visibility? Discover actionable SEO tips for beginners that will help you rank higher, drive more traffic, and grow your online presence.”
Visual Optimisation
Images and videos are powerful tools for enhancing your content, but they need to be optimised for SEO to prevent slow load times and accessibility issues.
Here’s how to make your visuals work in your favour:
Use Descriptive File Names: Before uploading an image, rename the file to something descriptive and relevant to the content. For example, instead of “IMG_001.jpg,” use “SEO-checklist-2024.jpg.”
Add Alt Text: Alt text is a brief description of your image that helps search engines understand what it represents. It’s also essential for screen readers, improving accessibility for visually impaired users. Be concise but include any relevant keywords naturally (again, don’t force it, this will do more harm than good, keep it natural!).
Compress Images for Faster Load Times: Large, high-resolution images can slow down your page, which can negatively impact your SEO. Use tools like TinyPNG or TinyJPG to compress images without sacrificing quality.
Note: Use PNG for images that need transparency and JPG/JPEG for ones that don't
Include Captions: When relevant, adding captions to images can help contextualise the visual for readers and search engines, this can improve engagement and comprehension.
Optimise Video Content: For video, use platforms like YouTube to host content and embed it into your page. Include a video transcript below the embedded video, as this can help search engines understand the video’s content and make it more accessible.
♻️ Repurposing Content for Maximum Reach
Repurposing content is like getting a second, third, or even fourth life out of your existing material. It’s about taking what you’ve already created and transforming it into different formats that reach a wider audience. Think of it as the ultimate way to squeeze more value from every piece of content you produce.
Let’s say you have a detailed blog post that performed well. Why not turn that blog post into:
A video or webinar: Visual content is highly engaging and perfect for platforms like YouTube or your social media channels. This content can be sliced and diced for shorter snippets for social media or used as longer form content for Youtube to help diversify your audience across different platforms and media formats.
An infographic: This makes complex information more digestible and shareable, which is great for driving traffic back to your site and earning backlinks. This has been a solid tactic for some time now in earning backlinks through creating shareable content.
A podcast episode: If you have a regular podcast, use the blog’s key points as a topic for discussion. Podcasts are a great way to reach a different audience who may prefer listening over reading – especially if you have identified that your target audience is time poor.
Repurposing content extends its shelf life and helps you tap into other audience preferences. Plus, different formats perform better on different platforms, so this strategy increases your chances of ranking across multiple channels, not just search engines.
🤖 The Role of AI in Content and SEO
AI is no longer the stuff of science fiction – it’s here, and it’s transforming the way we create and optimise content. Tools like ChatGPT and Gemini have made it easier than ever to generate ideas, write drafts, and even refine SEO elements without breaking a sweat. But like any tool, AI comes with its strengths and limitations.
One of the biggest benefits of AI is its ability to supercharge your content ideation process. Whether you’re brainstorming blog post topics, crafting meta descriptions, or identifying trending keywords (just make sure to combine this with a touch of reality by using tools like Google Trends and Exploding Topics to validate any trends).
AI might be able to save you hours of manual work by generating relevant suggestions in seconds – but proceed with caution, without combining it with human input you run the risk of being led off course. We cannot stress this enough, AI is a tool, not a replacement.
AI can also help you optimise your content with SEO by suggesting improvements like better keyword placement, title adjustments, CTA variations, or meta descriptions. Just remember to sense check anything that comes from an AI tool, while it may be impressive it still isn’t quite there yet.
While AI tools are great for scaling and efficiency, it’s essential to remember that they’re not a replacement for the human touch. AI might generate text that reads well, but it lacks the nuance and creativity that comes from a deep understanding of your brand and audience. Over reliance on AI can lead to generic content that doesn’t stand out or connect with your readers on a personal level.
The key is to use AI as a collaborator, not a crutch. Let it handle the repetitive tasks while you focus on adding the heart, soul, and strategic thinking that turns good content into exceptional content.
AI Prompts to Support Your SEO Content Development
Here are some of my tried and tested AI prompts for helping with content development, add or modify the information in the [square brackets] to suit what you are trying to create. I cannot stress enough how important it is to provide as much detail as you can with very specific requests in order to get the best output. This really is the epitome of “you get out what you put in”.
Content Outlines, Briefs and Writing
Content Brief Template:
Create a content brief template for [SEO content], think about what would be important to include in this, such as the target keywords, the pain points for the audience and persona, their challenges and motivations.
Content Brief / Outline:
Create a content brief and outline for a [blog post] based on these ranking URLs:
[Provide it with a list of 3-5 ranking URLs]
Think about how these [blogs] are structured, and why they rank well, what kind of person would get value from this content and how more value can be added that doesn’t exist in the ranking articles currently.
Meta Descriptions and Excerpts
Content Excerpt:
Write a short excerpt for [blog post title]. This will be used on the [blog home page] and should entice the user to want to read the [blog post] by covering what is in the content.
[Provide either the content outline or the full content in the prompt to provide enough information for a better output]
Meta Description:
Suggest a meta description for the content we have created. Think about what would be engaging and entice clicks. Keep the length under 160 characters to avoid this being truncated. Focus on wording that is human centric and provide 3 or 4 alternatives for me to select from.
Note: if you have not sent this prompt in the same chat make sure you provide the content in your prompt, or an overview of what it covers, as this context will be required for the best output.
Part 5: 🚫 Common SEO Optimisation Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
No matter how much experience you have with content marketing and SEO, it’s easy to fall into some common traps that can sabotage your efforts. Sometimes, even the most well intentioned strategies can backfire if you’re not careful. Most of these mistakes are entirely avoidable once you know what to look out for.
Let’s dig into some of the more common issues that can derail your content’s success and how to steer clear of them.
Focusing Solely on Keywords
One of the biggest mistakes brands make in their SEO strategy is becoming overly obsessed with keywords. Yes, keywords are essential – they help search engines understand the topic of your content and match it with user queries.
But there’s a catch: when you focus solely on cramming keywords into your content, you end up sacrificing the most important things – readability and user experience.
Keyword stuffing or over optimisation makes your content sound robotic and unnatural – it can do some serious damage, hurting your SEO rankings. Google’s algorithms are sophisticated enough to detect when keywords are being forced into content without adding any real value. Instead of trying to game the system, focus on creating content that answers your audience’s questions naturally and in depth.
Remember, your goal isn’t just to rank for keywords; it’s to connect with real people who find your content genuinely helpful. Let your content guide your keyword strategy, not the other way around. Keywords should enhance your content, not dictate it. Aim for a natural flow that prioritises clarity and value over exact match phrases. This approach improves readability and signals to search engines that your content is more focused on quality than trying to game the system.
Neglecting User Experience (UX)
Creating high quality content is only part of the equation; how your audience interacts with that content is equally as important. User Experience (UX) plays a massive role in how well your content performs. Even if your content is optimised and informative, poor UX can mean visitors leave your site without taking any meaningful actions and with a less than ideal first impression of your business.
A cluttered page layout, too many ads, or difficult to navigate menus can frustrate users and send them packing. Think about it this way: if your website feels like a maze, why would anyone stick around? Instead, aim for a clean, intuitive design that guides visitors smoothly from one piece of content to another, gently nudging them towards conversion points or into your nurture flow.
Load times also have a huge impact on UX. Even a delay of a few seconds can lead to visitors abandoning your page. The faster your site, the more likely users are to engage with your content and explore further.
Another major aspect of UX is responsive design – your content should look and perform just as well on a smartphone as it does on a desktop. Google has been on a mobile-first basis for a while now, taking the mobile experience as the default for your site, so if this isn’t a reflection of the desktop experience you might be suffering because of it. With search engines placing a growing emphasis on mobile experience, a seamless and responsive design is a core requirement.
Part 6: Post-Publishing Optimisation
Publishing your content is just the beginning. To make sure your hard work pays off, you need to promote it effectively and continue optimising it over time. Think of this as the maintenance phase of your SEO strategy, where the right tweaks and strategic distribution can help you maximise reach, keep your rankings strong, and ensure your content stays relevant.
Let’s walk through key steps for post publishing optimisation that will help your content perform better after it goes live.
Content Promotion
Once your content is live, the next step is getting it in front of the right audience. Effective promotion is essential for driving traffic, increasing shares, and building authority in your niche.
Here are some tips for content distribution:
Social Media: Share your content across your brand’s social media platforms (LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, etc.) to reach your existing audience. Tailor your message for each platform – for example, on LinkedIn, you might focus on a more professional angle, while X (formerly Twitter) could highlight a catchy or insightful quote. Don’t hesitate to re-share evergreen content over time to keep it visible, especially if you have recently updated it.
Email Newsletters: Email still remains one of the more effective ways to connect with an engaged audience. Send your content to your subscribers with an engaging subject line, a brief summary, and a clear call-to-action to drive clicks. For regular updates, consider creating a monthly “Top Resources” email or even segmenting your list to send specific content to the most relevant readers.
Influencer Outreach: If you’ve created a unique or highly valuable piece of content, consider reaching out to industry influencers who may find it helpful. You could offer to collaborate on future content, or simply ask them to share it if they find it useful. Be genuine and avoid cold, impersonal messages – personalise your outreach to build authentic relationships.
Communities and Forums: For niche topics, online communities (like Reddit, industry forums, or Quora) can be great places to share content. Be mindful of community guidelines, and focus on genuinely adding value rather than just promoting your link.
Paid Promotion: For high priority content, you might want to consider using paid channels like Facebook Ads, Google Ads, or sponsored posts on LinkedIn. Targeted ads can be an effective way to increase visibility, especially for content that aligns with product launches, campaigns, or seasonal trends. This can become a bit of a drain on budget so make sure you have all of your ducks in a row and a plan for how this will translate into conversions or sales and a clear goal and KPIs. Typically this tactic is reserved for bigger campaigns and plays into a larger strategy, either to boost brand awareness or to compete in a highly competitive SERP (search engine results page).
Pro Tip: Use UTM tracking on your links to measure the effectiveness of each promotion channel. This helps you see which sources bring in the most traffic and allows you to adjust your strategy accordingly.
To keep your content relevant and maintain traffic, you should invest in regular updates. Google values fresh, up-to-date information, and a well maintained post often outperforms even newly published content.
By actively promoting and periodically updating your content, you can extend its life cycle, attract more visitors, and keep your site’s performance strong over time. Remember, post-publishing optimisation is as important as the initial publishing itself, so keep the momentum going long after hitting “publish.”
Over to you
Now that you have the insights and tools for creating and optimising SEO content, it’s time to put these strategies into action. Start with a single piece of content, apply these techniques, and monitor the results. Creating SEO content that drives traffic, builds authority, and resonates with your audience might seem complex, but with a solid strategy and some key techniques, you’re set up for success. Over time, you’ll not only see improvements in your rankings and traffic but also develop a deeper understanding of your audience and how to meet their needs more effectively.
Download your SEO Copywriting Cheatsheet
Additional Resources for Diving Deeper
For those keen to expand their SEO knowledge, here are some resources and tools to guide you further:
Google Search Central: Google’s official hub for SEO resources, updates, and best practices.
Ahrefs and SEMrush Blogs: Both of these platforms offer detailed guides and articles on SEO techniques, keyword research, and content marketing.
Google Analytics Academy: Free courses from Google that teach you how to make the most of Google Analytics.
Moz’s Beginner’s Guide to SEO: A comprehensive starting point for anyone new to SEO.
SEO is a journey of constant learning and adjustment, but with these techniques, you’re ready to create content that performs. Keep experimenting, keep optimising, and watch as your content becomes a powerful driver of growth for your site.